Unveiling the Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Simplified

Photosynthesis is one of the most vital processes on Earth, allowing plants to convert sunlight into energy. Understanding the chemical equation for photosynthesis is key to grasping how this process sustains life. In this post, we’ll break down the equation in simple terms, explore its components, and provide actionable insights for both informational and commercial audiences.
What is the Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis?
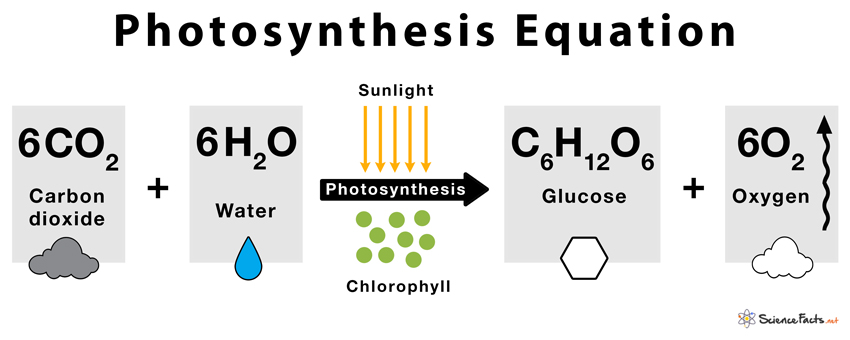
The chemical equation for photosynthesis is a fundamental concept in biology. It describes how plants, algae, and some bacteria convert carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) into glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and oxygen (O₂) using sunlight. The simplified equation is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation highlights the role of light energy in driving the reaction, making it a prime example of a light-dependent reaction.
📌 Note: The equation represents the overall process, but photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle.
Breaking Down the Components

To fully understand the chemical equation for photosynthesis, let’s examine its key components:
Reactants
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Absorbed from the atmosphere through tiny pores called stomata.
- Water (H₂O): Drawn from the soil via the plant’s roots.
- Light Energy: Captured by chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
Products
- Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): The primary energy source for plants, stored as starch.
- Oxygen (O₂): Released as a byproduct, essential for most living organisms.
| Component | Role in Photosynthesis |
|---|---|
| CO₂ | Carbon source for glucose synthesis |
| H₂O | Provides hydrogen and electrons for the process |
| Light Energy | Drives the reaction by exciting chlorophyll molecules |

Why is the Chemical Equation Important?

For informational-intent visitors, understanding the chemical equation for photosynthesis sheds light on how plants produce food and oxygen. For commercial-intent visitors, this knowledge is crucial for industries like agriculture, renewable energy, and environmental science.
- Agriculture: Optimizing crop yields by enhancing photosynthesis efficiency.
- Renewable Energy: Developing biofuels and solar technologies inspired by photosynthesis.
- Environmental Science: Addressing climate change by studying carbon sequestration.
Simplifying Photosynthesis for Practical Use

Whether you’re a student, researcher, or entrepreneur, simplifying the chemical equation for photosynthesis can help you apply this knowledge effectively. Here’s a checklist to guide you:
- Learn the Equation: Memorize 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂.
- Understand Reactants and Products: Identify their roles in the process.
- Explore Applications: Investigate how photosynthesis impacts your field.
📌 Note: For commercial applications, consider tools and technologies that mimic or enhance photosynthesis, such as artificial leaves or LED grow lights.
The chemical equation for photosynthesis is more than just a formula—it’s the foundation of life on Earth. By understanding its components and applications, you can appreciate its significance in both natural and industrial contexts. Whether you’re studying biology, working in agriculture, or exploring renewable energy, this knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions.
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
+The chemical equation for photosynthesis is 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂.
Why is oxygen released during photosynthesis?
+Oxygen is released as a byproduct when water molecules are split during the light-dependent reactions.
How does photosynthesis impact climate change?
+Photosynthesis reduces CO₂ levels by converting it into glucose, helping mitigate greenhouse gas effects.
chemical equation for photosynthesis,photosynthesis process,light-dependent reaction,chlorophyll function,carbon sequestration,renewable energy,agricultural optimization,environmental science,glucose synthesis,oxygen production.

